Introduction
India is experiencing an unprecedented surge in solar power adoption, reinforcing its commitment to a greener and more sustainable future. As of February 2025, the country’s solar capacity has reached 102.57 GW, with 2,236.02 MW added in just one month! This rapid expansion is not just a milestone but a testament to India’s ambition to lead the global clean energy revolution.
A major contributor to this progress is the PM Surya Ghar Initiative, which has witnessed a significant number of applications, installations, and subsidies disbursed for rooftop solar adoption. With increasing policy support, private sector participation, and technological advancements, India is well on its way to achieving its ambitious 280 GW solar target by 2030.

Breaking Down the Numbers
The current solar power landscape in India is diverse and rapidly evolving. Here’s how the installed capacity is distributed across different categories:
✅ Ground-mounted Solar – 78.47 GW (76.5%)
✅ Rooftop Solar – 16.66 GW (16.2%)
✅ Hybrid Projects – 2.85 GW (2.8%)
✅ Off-grid Solar – 4.59 GW (4.5%)
With strong government policies and increasing private investments, these numbers are set to grow exponentially in the coming years.
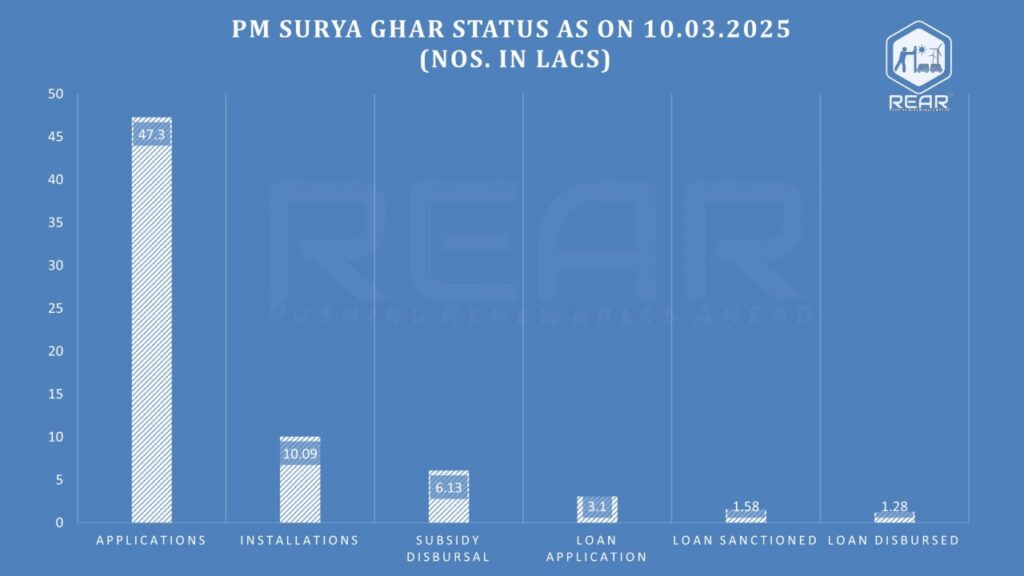
PM Surya Ghar Initiative: Status Update (As of March 10, 2025)
One of the key programs driving rooftop solar adoption in India is the PM Surya Ghar Initiative. Here’s an update on its progress:
- Applications Received – 47.3 lakh
- Installations Completed – 10.09 lakh
- Subsidy Disbursed – 6.13 lakh
Key Insights:
✅ A high number of applications (47.3 lakh) indicates strong interest in rooftop solar adoption.
✅ However, only 10.09 lakh installations have been completed, suggesting possible delays in execution.
✅ Subsidy disbursal (6.13 lakh) is progressing but needs to be expedited to encourage wider adoption.
What’s Driving India’s Solar Boom?
Several factors have contributed to this remarkable growth in solar energy adoption:
1. Policy Support & Government Initiatives
The Indian government has launched multiple schemes to promote solar energy, including:
- PM-KUSUM Scheme – Supporting farmers with solar irrigation pumps.
- PM Surya Ghar – Muft Bijli Yojana – The PM Surya Ghar – Muft Bijli Yojana, along with PM-KUSUM, Solar Parks, the PLI Scheme, and Net Metering policies, is driving India towards a solar-powered future
- Solar Park Development – Boosting large-scale solar installations.
- PLI Scheme for Solar Modules – Encouraging domestic manufacturing of solar panels.
Net Metering Policies – Making rooftop solar adoption easier for residential users.
2. Falling Costs of Solar Power
The cost of solar energy has declined by over 80% in the last decade, making it one of the most affordable sources of electricity. Lower equipment costs, economies of scale, and technological advancements have made solar energy more accessible to businesses and homeowners.
3. Increased Corporate & Residential Adoption
More industries and commercial establishments are switching to solar to reduce electricity costs and meet sustainability goals. Residential solar adoption is also gaining momentum due to attractive subsidies, net metering policies, and rising awareness of renewable energy benefits.
4. Energy Independence & Sustainability Goals
India aims to achieve 280 GW of solar capacity by 2030, forming the backbone of its renewable energy strategy. By reducing dependence on fossil fuels, India is moving towards greater energy security and a low-carbon economy.

The Road Ahead: Challenges & Opportunities
While India’s solar journey is impressive, some challenges still need to be addressed:
- Land Acquisition Issues – Finding suitable land for large solar farms remains a challenge.
- Grid Integration & Storage – Managing intermittent solar power requires better storage solutions and grid upgrades.
- Financing & Investments – Access to affordable financing for small businesses and homeowners can boost adoption.
Potential Areas of Focus:
- Faster Approvals & Installations – Reducing processing times for rooftop solar installations can help bridge the gap between applications and execution.
- Streamlining Subsidy & Easy Finance option – Ensuring timely financial support will accelerate adoption, especially in the residential sector.
- Awareness & Accessibility – Addressing concerns related to financing, paperwork, and grid integration can further boost adoption rates.
Conclusion: A Solar-Powered Future Awaits
India’s solar power boom is more than just a statistic—it’s a movement towards a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable future. With solar adoption accelerating at an incredible pace, it’s time for businesses, homeowners, and policymakers to come together and make the most of this energy revolution.
What do you think about India’s solar growth? Are we ready to surpass 280 GW by 2030? Let us know in the comments!
Contact Solar Smart Pvt. Ltd. today and become a part of Ahmedabad’s solar-powered future!
Call us: 079 6900 7700
Visit us: https://solarsmart.co.in

